Di-layers satellite electronic shielding system (DiLSES): fabrication and characterization
Keywords:
Satellites, Space radiation, Linear attenuation, Beta radiationAbstract
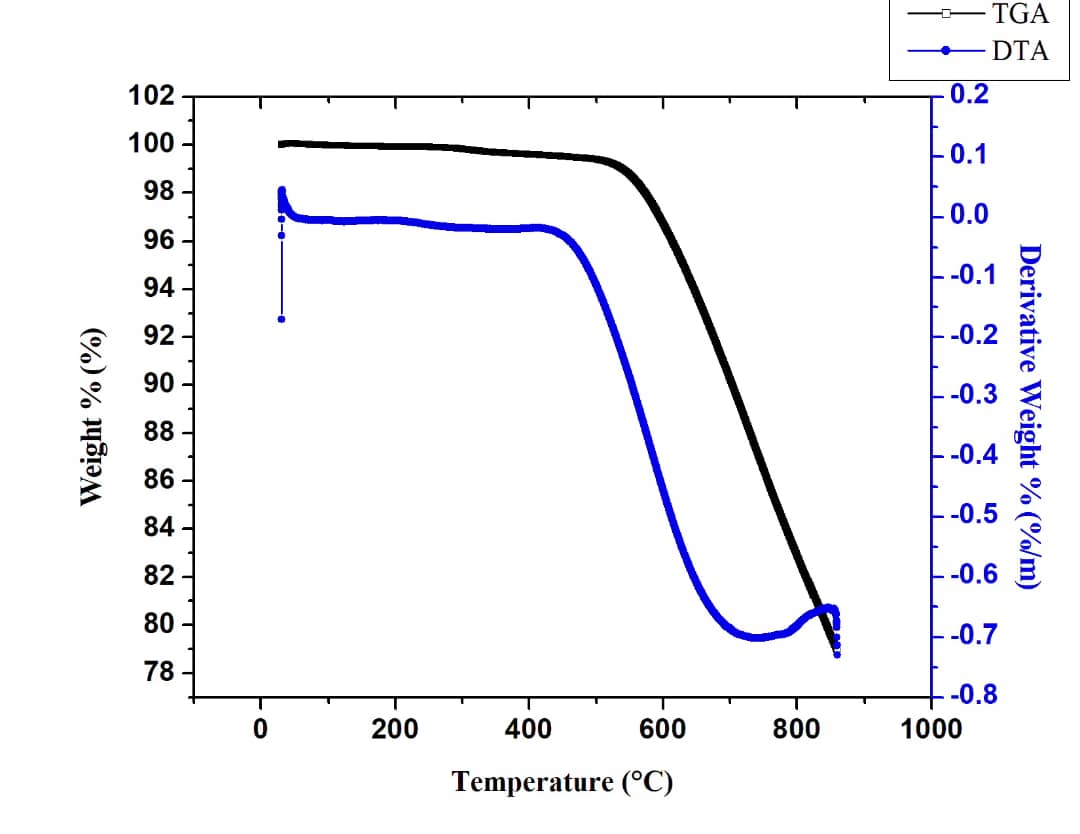
Satellites in space are vulnerable to high-energy electrons above that can damage their electronic systems. To curtail this challenge, a new multi-layer system is synthesized from biomass and geological ores and characterized for mechanical, thermal as well as gamma and beta radiation shielding efficiencies. The new system, a Di-layer Satellite Electronic Shielding System (DiLSES), featuring an innovative, light weight, two-layer material composite made from low atomic number material labeled which are arranged in two configurations LH and HL. This advanced material shows exceptional mechanical characteristics with impact strength of hardness of and tensile strength of, making it resistant to launch vibrations and collision with low velocity space debris. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) revels that DiLSES can withstand high temperature environment of up to 300 and only gradually decomposes by less than 5% between and For gamma radiation shielding efficiency, the DiLSES effectively attenuated pointed gamma radiation from Co-60 with maximum energy of 1.332 MeV by and for and the LH configuration offers better attenuation. The DiLSES attenuates high-energy beta particles generated by medical LINAC by over 93%, achieving a remarkable reduction at energy .This innovative light-weights and cost-effective material has the potential to improve the shielding of electronic components in satellites against high-energy beta particles (greater than 1 Mev) which cause satellite damage and operational failures. It also offers protection from space radiation like gamma and cosmic rays, making it useful for both space and medical applications.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Emmanuel Ochoyo Adamu, Abubakar Sadiq Aliyu, Abdulkarim Muhammad Hamza, Muhammad Sani, Umar Sa’ad Aliyu, Mngusuur Scholastica Iorshase, Lubem James Utume, Wasiu Oyeyemi Salami, Isaac Pada, Emmanuel Ogwuche (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




