High performance multilayer satellite electronic shielding system (MULSES)
Keywords:
Satellites, Space radiation, Linac, HDPe, BiomassAbstract
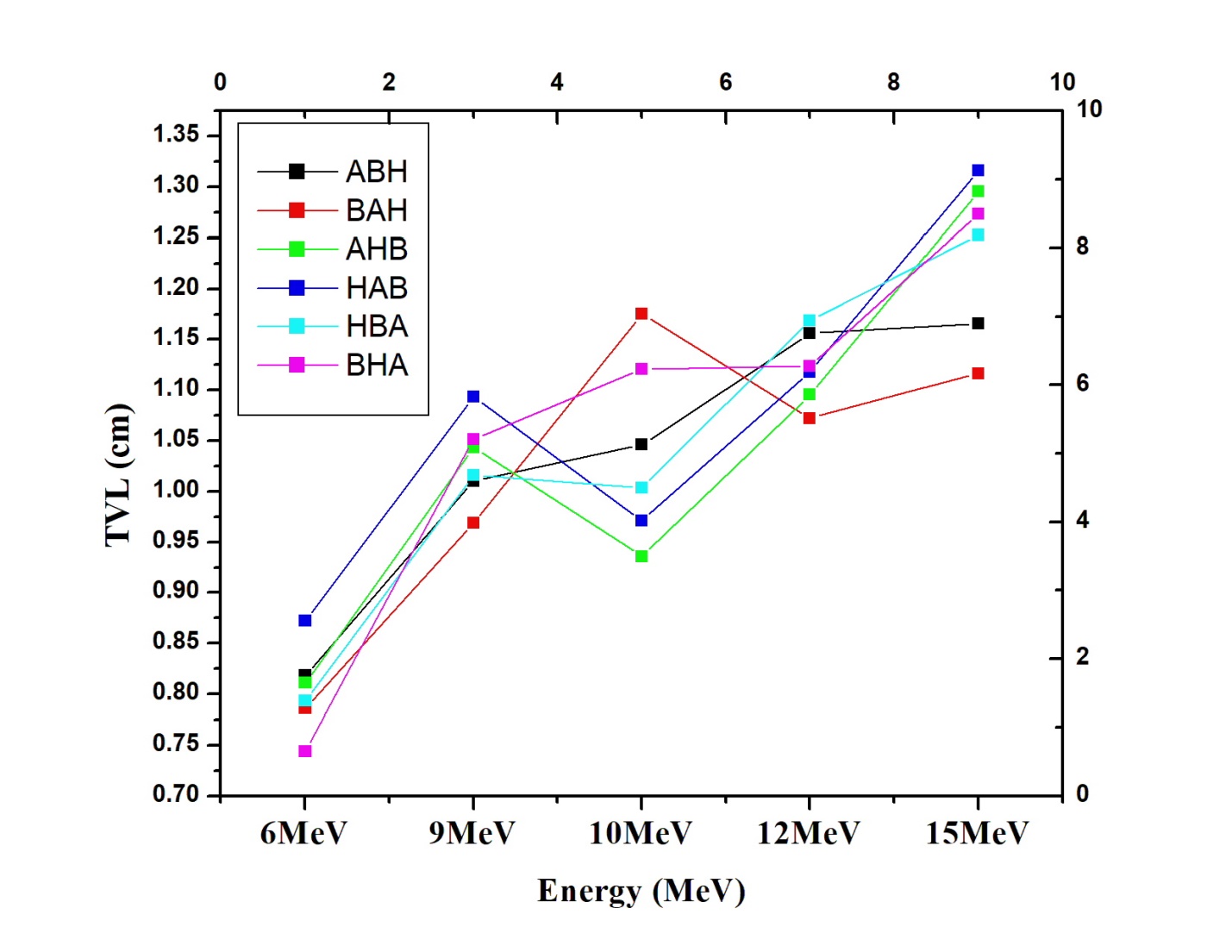
Passive radiation shielding has gained prominence in space technology due to satellite malfunction and destruction by high-energy beta particles in low Earth orbit (LEO). This paper describes the synthesis and characterization of a novel composite material composed of aluminum oxide (Al2 O3 ), hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), and high-density polyethylene (HDPe) reinforced with Doum fiber. MULSES mechanical properties exhibited tensile strength of 25 MPa, hardness of 85.7 Hv, and impact energy absorption of 23.721 J, demonstrating a perfect combination of strength, flexibility, and toughness. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) showed the composite has thermal stability until approximately 600◦ C, degradation was initiated at 320◦ C and optimal degradation was at 480◦ C. Differential thermal analysis (DTA) showed peaks of exothermic degradation at 400◦ C and 520◦ C corresponding to decomposition of polymer and fibers, respectively, and show the suitability of the composite to handle high temperature. Radiation shielding efficiency was tested at various beta (6, 9, 10, 12, and 15 MeV) and gamma (662 keV and 1.25 MeV) energies. Stacking arrangement played a crucial role in shielding efficiency, with the BHA (Boron, HDPe, Aluminum) arrangement delivering the maximum beta radiation protection efficiency (RPE) of 99.16% at 6 MeV and 95.42% at 15 MeV. When compared to other stack arrangements, the BHA arrangement showed 12% improvement in beta attenuation efficiency and 8% improvement in gamma attenuation efficiency. The smaller mean free path (MFP) and half-value layer (HVL) for beta and gamma radiation also confirm the improved shielding property of the BHA arrangement. HDPe-Doum fiber-h-BN-Al2 O3 exhibits the optimum mechanical strength, heat stability, and radiation shielding properties all together that render MULSES a cost-effective, light, and renewable space shielding material.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Lubem James Utume, Abubakar Sadiq Aliyu, Abdulkarim Muhammad Hamza, Muhammad Sani, Umar Sa’ad Aliyu, Mngusuur Scholastica Iorshase, Emmanuel Ochoyo Adamu, Wasiu Oyeyemi Salami, Isaac Pada, Emmanuel Ogwuche (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




