Comparative studies for determining the optical band gap energy of CuSe thin films
Keywords:
Selenium, Tauc’s relation, Band gap, Structural property, Thermal evaporationAbstract
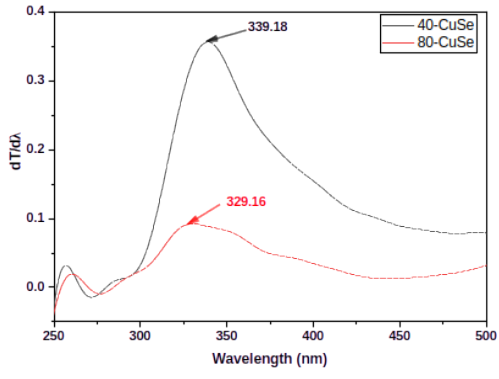
In the present study, copper selenide (CuSe) metal chalcogenide thin films have been fabricated from Se/Cu bilayer deposited using two-step procedure involving thermal evaporation and dip coating followed by thermal annealing. The thermally evaporated Se layer was maintained at a constant thickness of 40 nm while the dip coated layer of copper was carried out for varying time of 40 and 80 min. The prepared CuSe thin film was characterized in terms of its structural and optical properties. The X-ray diffraction spectra revealed post thermal inter-diffusion of the two layers and the production of CuSe thin film exhibiting hexagonal crystal structure. The optical transmission measurements were recorded within the wavelength range of 300 to 1000 nm. Four different methods were employed in ascertaining the direct band gap energies of the prepared CuSe thin films and the results were compared with the famous Tauc’s relation. The values of the band gap energy ranges between 3.58 and 3.87 eV for the 40-CuSe sample as well as 3.65 and 3.99 eV for the 80-CuSe sample. The results from the study confirmed that the fabricated films possess wide band gap energy, making them a candidate for window layer in many solar cell applications.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 O. O. Olasanmi, S. I. Akinsola, K. A. Yusuf, A. E. Aregbesola (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




