Spectroscopic characterization of a derivative of naphthalene isolated from Hibiscus sabdariffa calyx
Keywords:
Hibiscus sabdariffa, Naphthalene derivative, chromatographic separation, 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopyAbstract
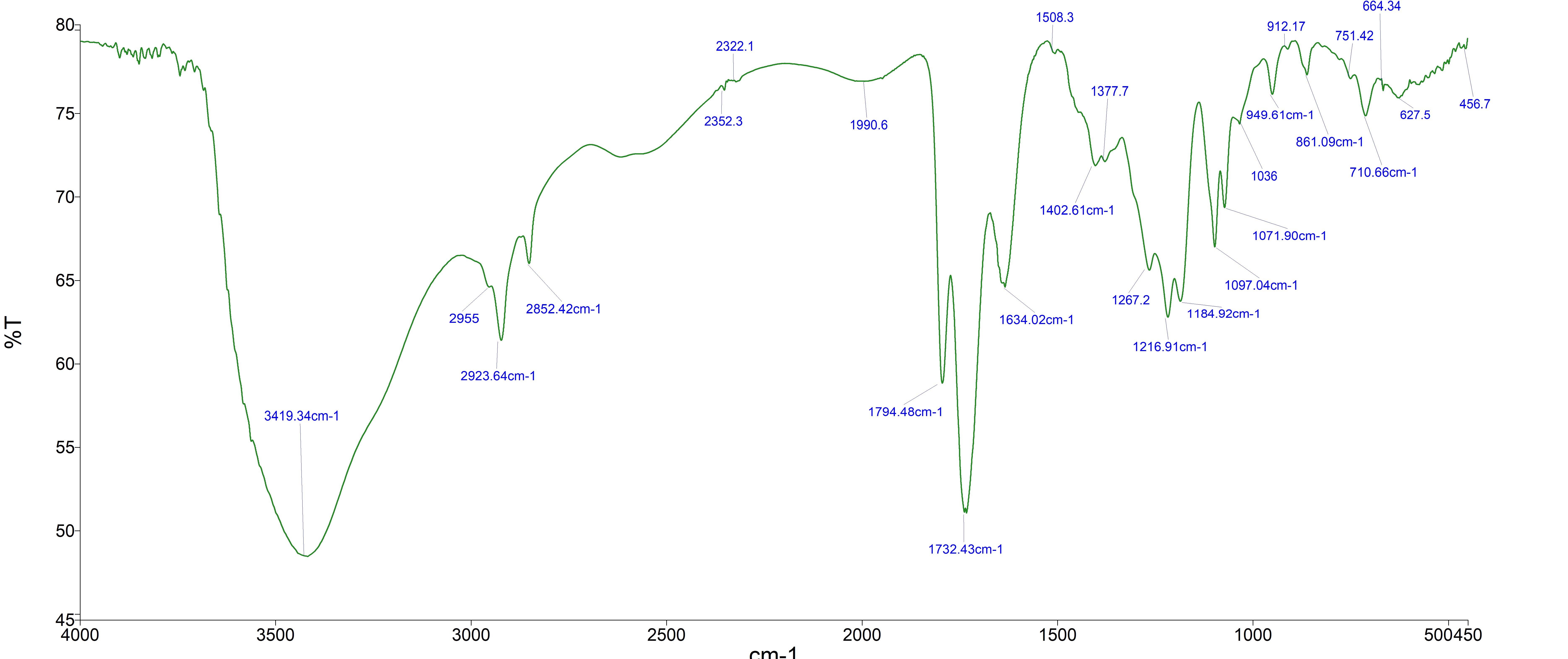
Hibiscus sabdariffa (Hs) is a nutritive and medicinal herb that belongs to the Malvaceae family. It is mainly composed of organic acids, anthocyanins, polysaccharides and flavonoids. Hibiscus sabdariffa, being a natural source of bioactive compounds made up of several reactive functional groups, could serve the purpose of a starting material in the production of other compounds. Acidified aqueous ethanol extract of Hs was subjected to column chromatographic fractionation that yielded a yellow liquid isolate, which was characterized by UV–Visible, Infrared spectroscopy, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HRMS). The NMR spectra displayed distinct signals of a naphthalene ring linked through a carbonyl carbon to a napht 2 –yl moiety. 1H and 13C NMR indicated the presence of five aromatic protons (dH 6.98 – 7.51) resonating with ten aromatic carbon atoms (dc100.0 – 177.9), (C 189.2, indicating the presence of a carbonyl carbon coupled with a hydrogenated naphthalene ring substituent. Absorptions at 304nm, 366 nm and 506nm are due to pi- pi∗ and n - pi∗ , respectively. IR peak at 2923 cm-1 is ascribed to C − H stretch, while the peak at 1732(s) cm-1, with shoulders at 1634(w) and 1794(w), affirmed the presence of carbonyl functional group conjugated to an unsaturated naphtalen-2yl ring system. The isolated naphthalene derivative is characterized as ‘3 methyl-1, 4, 4a, 5, 6, 7, 8, 8a, octahydronaphtalen-2-yl)(naphtalen-2yl)methanone.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2026 Adewumi Idowu Adeagbo, Adekunle Abeeb Azeez

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







